Since the new year, your inbox has probably become acquainted with the phrase, “privacy policy update.” For this, you can blame California’s new privacy law, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), that went into effect January 1st, greatly affecting the ways companies collect and store consumer data. The CCPA can affect all businesses online, regardless of your home state or country, depending on where your users are from and what data you collect. That’s why it’s vital, regardless of your locale, to understand the CCPA inside and out.
What is the CCPA?
Seen by some to be in response to Facebook’s Cambridge Analytica scandal, the CCPA is a statute meant to reinforce the privacy rights and consumer protection of California residents. With this act comes several new privacy rights for the people of California. Specifically, California residents have the right to:
- Know what personal data is being collected.
- Know if and to whom their personal data is being sold.
- Deny the sale of personal data.
- Retrieve their personal data.
- Order a business to delete any personal information about them.
- Exercise these rights without discrimination.
What Businesses are Affected by the CCPA?
The CCPA requires compliance from any organization that does business in California and fulfills any of the following:
- Stores more than 50,000 people’s personal data.
- Has an annual gross revenue of $25 million.
- Generates more than 50% of their annual revenue from selling personal data.
Is This California’s Version of the GDPR?
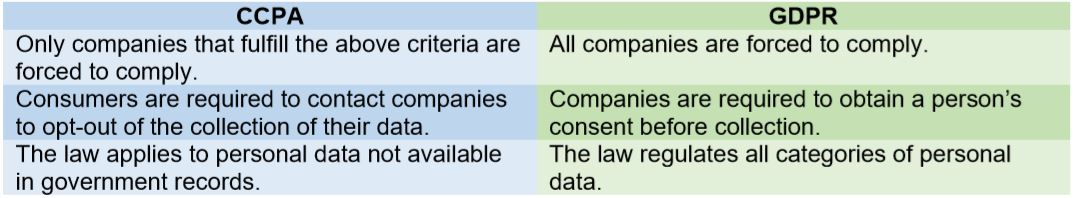
In 2018, you may remember the European Union introducing the strongest data protection rules in the world in the form of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). While the two laws are similar, in that they both address the collection and storage of personal data, they have a few significant differences.
What is Considered Personal Data Under the CCPA?
“Personal data” is a pretty vague term as is, but compared to the GDPR, the CCPA has an even broader definition, which is why it’s important to dissect what it entails. Personal data refers to anything that can identify – or can be specifically associated with – an individual or household. Of course, there are the obvious components – names, addresses, phone numbers, and all forms of identification numbers – but there are lesser-known identifiers, such as follows:
- Physical and behavioral characteristics
- Geolocation data
- Employment or education-related information
However, there are some notable exemptions: any data that is already publicly available from government records is not considered protected personal information. Also, the CCPA is not responsible for information already covered under current California laws, such as protected health information or financial information.
While the influx of privacy policy update emails is a nuisance, it’s essential to understand what has changed under the California Consumer Privacy Act. No matter where your business is located, you are responsible for abiding by the laws of governing bodies outside your state when dealing with consumers. For help properly collecting and storing data and for all your website, social media, and email marketing needs, don’t hesitate to contact us at Vision. And for more information on the CCPA and its effects on your business, read our blog, Keeping in Compliance with the CCPA.